Generate Aes Key In Java
In order to be able to create a digital signature, you need a private key. (Its corresponding public key will be needed in order to verify the authenticity of the signature.)
In some cases the key pair (private key and corresponding public key) are already available in files. In that case the program can import and use the private key for signing, as shown in Weaknesses and Alternatives.
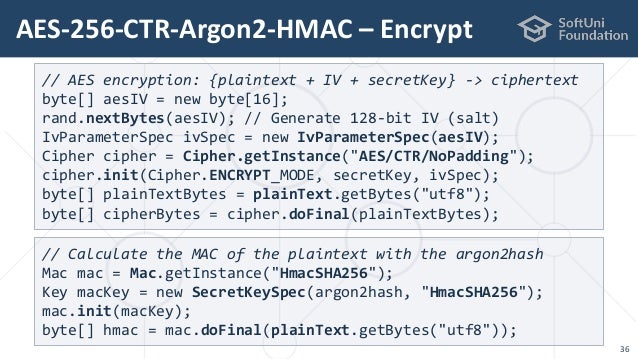
Using the KeyGenerator class and showing how to create a SecretKeySpec from an encoded key. AES Key generator: 36.2.3. Tampered message, plain encryption, AES in CTR mode: 36.2.4. Tampered message, encryption with digest, AES in CTR mode: 36.2.5. Tampered message with HMac, encryption with AES in CTR mode: 36.2.6. AES wraps RSA. AES uses 128-bit keys, i.e. Sequences of 128 bits. How you come up with such a key is out of scope of AES. How you come up with such a key is out of scope of AES. In some contexts, you want to generate these 128 bits in a deterministic way from a password (and possibly some publicly known contextual data, like a 'salt'); this is a job for. To generate secrete key we can use Java KeyGenerator class which provides the functionality of a secret (symmetric) key generator. Key generators are constructed using one of the getInstance class methods of this class. GetInstance method of KeyGenerator takes parameter name of algorithm and Returns a KeyGenerator object that generates secret keys for the specified algorithm. You can use the keytool shipped with the encryption proxy distribution to create AES 128-bit and AES 256-bit encryption keys. Product documentation Docs. Create encryption keys using the Java KeyStore keytool. Save as PDF Selected topic Topic & subtopics All topics in contents. Mar 12, 2020 Generating AES keys and password Use the OpenSSL command-line tool, which is included with InfoSphere® MDM, to generate AES 128-, 192-, or 256-bit keys. The madpwd3 utility is used to create the password. GenerateDataKey returns a unique data key for each request. The bytes in the key are not related to the caller or CMK that is used to encrypt the data key. Use AES128 to generate a 128-bit symmetric key, or AES256 to generate a 256-bit symmetric key. AWS SDK for Java.
In other cases the program needs to generate the key pair. A key pair is generated by using the KeyPairGenerator class.
In this example you will generate a public/private key pair for the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA). You will generate keys with a 1024-bit length.
Generating a key pair requires several steps:
Create a Key Pair Generator
The first step is to get a key-pair generator object for generating keys for the DSA signature algorithm.
As with all engine classes, the way to get a KeyPairGenerator object for a particular type of algorithm is to call the getInstance static factory method on the KeyPairGenerator class. This method has two forms, both of which hava a String algorithm first argument; one form also has a String provider second argument.
A caller may thus optionally specify the name of a provider, which will guarantee that the implementation of the algorithm requested is from the named provider. The sample code of this lesson always specifies the default SUN provider built into the JDK.
Put the following statement after the
line in the file created in the previous step, Prepare Initial Program Structure:
Initialize the Key Pair Generator
The next step is to initialize the key pair generator. All key pair generators share the concepts of a keysize and a source of randomness. The KeyPairGenerator class has an initialize method that takes these two types of arguments.
The keysize for a DSA key generator is the key length (in bits), which you will set to 1024.
The source of randomness must be an instance of the SecureRandom class that provides a cryptographically strong random number generator (RNG). For more information about SecureRandom, see the SecureRandom API Specification and the Java Cryptography Architecture Reference Guide .
The following example requests an instance of SecureRandom that uses the SHA1PRNG algorithm, as provided by the built-in SUN provider. The example then passes this SecureRandom instance to the key-pair generator initialization method.
Some situations require strong random values, such as when creating high-value and long-lived secrets like RSA public and private keys. To help guide applications in selecting a suitable strong SecureRandom implementation, starting from JDK 8 Java distributions include a list of known strong SecureRandom implementations in the securerandom.strongAlgorithms property of the java.security.Security class. When you are creating such data, you should consider using SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong(), as it obtains an instance of the known strong algorithms.
Generate the Pair of Keys
The final step is to generate the key pair and to store the keys in PrivateKey and PublicKey objects.
If a code signer does not yet have a suitable private key for signing the code, the key must first be generated, along with a corresponding public key that can be used by the code receiver's runtime system to verify the signature.
Since this lesson assumes that you don't yet have such keys, you are going to create a keystore named examplestore and create an entry with a newly generated public/private key pair (with the public key in a certificate).
Type the following command in your command window to create a keystore named examplestore and to generate keys:
You will be prompted to enter passwords for the key and keystore.
Subparts of the keytool Command
Let's look at what each of the keytool subparts mean.
- The command for generating keys is -genkey.
- The -alias signFiles subpart indicates the alias to be used in the future to refer to the keystore entry containing the keys that will be generated.
- The -keystore examplestore subpart indicates the name (and optionally path) of the keystore you are creating or already using.
- The storepass value that you are promted for specifies the keystore password.
- The keypass value that you are prompted for specifies a password for the private key about to be generated. You will always need this password in order to access the keystore entry containing that key. The entry doesn't have to have its own password. When you are prompted for the key password, you are given the option of letting it be the same as the keystore password.
Note: For security reasons you should not set your key or keystore passwords on the command line, because they can be intercepted more easily that way.
Distinguished-Name Information
If you use the preceding keystore command, you will be prompted for your distinguished-name information. Following are the prompts; the bold indicates what you should type.
Command Results
The keytool command creates the keystore named examplestore (if it doesn't already exist) in the same directory in which the command is executed. The command generates a public/private key pair for the entity whose distinguished name has a common name of Susan Jones and the organizational unit of Purchasing.
The command creates a self-signed certificate that includes the public key and the distinguished-name information. (The distinguished name you supply will be used as the 'subject' field in the certificate.) This certificate will be valid for 90 days, the default validity period if you don't specify a -validity option. The certificate is associated with the private key in a keystore entry referred to by the alias signFiles.

Generate Aes Key Java Example
Self-signed certificates are useful for developing and testing an application. However, users are warned that the application is signed with an untrusted certificate and asked if they want to run the application. To provide users with more confidence to run your application, use a certificate issued by a recognized certificate authority.
Generate Random Aes Key
Note: The command could be shorter if option defaults are accepted or you wish to be prompted for various values. Whenever you execute a keytool command, defaults are used for unspecified options that have default values, and you are prompted for any required values. For the genkey command, options with default values include alias (whose default is mykey), validity (90 days), and keystore (the file named .keystore in your home directory). Required values include dname, storepass, and keypass.