Generate Ssh Key Linux Gitlab
- Generate Ssh Key Ubuntu Gitlab
- How To Add Ssh Key To Gitlab
- Generate Ssh Key Windows
- Generate Ssh Key Gitlab
- Gitlab Create Ssh Key
- Sep 26, 2019 - By setting ssh key you can connect to GitLab server without using username and password each time Step 1: Run command ssh-keygen On Mac - run command on terminal.
- I have two Gitlab accounts. On my old account I added an ssh-key that is located in /.ssh/idrsa.pub on my computer. Now I want to add another ssh-key for my new Gitlab account. How do I do this.
- Dec 23, 2019 With the ssh key just in the folder, the push was not working on the Gitlab server. I had to “add” it in the clip with the previous command. I would like to.
The SSH stands for Secure Shell or Secure Socket Shell used for managing the networks, operating systems and configurations and also authenticates to the GitLab server without using username and password each time. You can set the SSH keys to provide a reliable connection between the computer.
Linux and Mac OS X both come with support for SSH and SSH keys out of the box. Launchpad uses SSH keys to authenticate your computer with your Launchpad account. This guide shows you how to get that done.
SSH Keys
The first thing you need to do is generate your SSH keypair. A keypair, as the name implies, consists of 2 parts: the public key and the private key.
Public Key
Your public key is placed on remote servers so that they can check back with you to see that you are who you say you are.
Private Key
Your private key should NEVER leave your computer! This is the main file that authenticates you. It contains the special unique data that identifies you.
Generating a Keypair
Generating a keypair is very easy.
- Open a terminal
- Enter in the following in the terminal:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 - Accept the defaults, to save your public and private keys to ~/.ssh
- Open your public key (~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub) in a text editor (GEdit or Kate on Linux, TextEdit on Mac OS X)
Launchpad & SSH
When you use Launchpad and Bazaar, it likes to use the SSH keys to authenticate you. We need to add our public key to Launchpad.
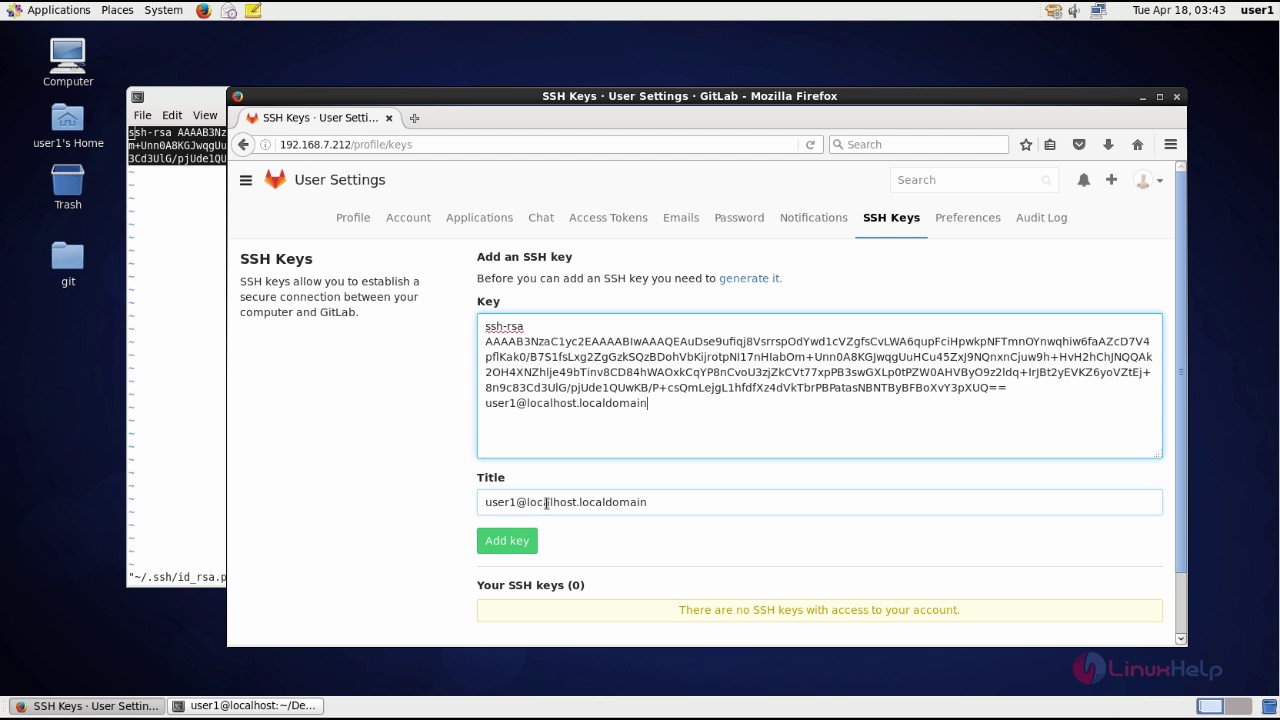
Adding Your Public Key to GitLab
- Open your browser to GitLab and log in
- Go to your home page and click on the 'Profile / Settings' link
- Click on the 'SSH Keys' tab (Note: not the OpenPGP keys!)
- Paste that public key into the text box at the bottom of the page
- Click the 'Add Key' button at the bottom of the page
And you're done!
More In Depth Example
This is specific to Mac OS X 10.6, but should be similar on any Mac or Linux system.
- Open Terminal
- Change to hidden SSH folder
$ cd ~/.ssh/ - Generate a key
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096Prompts for above are as follows, just hit enter for the file name, and then enter the password twice and you are done.- Enter file in which to save the key (/Users/username/.ssh/id_rsa): [Just Hit Enter]
- Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Enter a unique password]
- Enter same passphrase again: [Renter a unique password]
- Make sure you remember your password you enter
- Now you should have 2 new files in your folder, named id_rsa and id_rsa.pub which are your private and public keys respectively.
- Set permissions on the keys you just created to be as restrictive as possible.
chmod 400 id_rsa* - Modify the SSH config file to automatically use your just created key every time you connect to launchpad
- Use your choice of text editor to edit ~/.ssh/config
sudo vi config- Hit i to enter insert mode
- Add the following text to the bottom, where it says yourlaunchpdusername replace with your gitlab user name. ( to get yourgitlabname visit https://gitlab.com/~ and it will redirect to add your username to the url after the ~ )
Host bazaar.launchpad.net IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa User yourgitlabusername - Hit Escape
- Hit ZZ
- Copy the contents of your public key file on the Mac
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | pbcopyLinux users or Mac users can alternatively open ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub with your favourite text editor or omit pbcopy and just copy it after running the commandcat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. - Finally Edit your SSH keys on launchpad as described in Adding Your Public Key to GitLab above. ( you can click on This Link which will take you directly to the page to update your SSH keys on gitlab ). Make sure you are on SSH keys and not PGP keys here.
Generate Ssh Key Ubuntu Gitlab
Hello Everyone
Welcome to CloudAffaire and this is Debjeet.
In the last blog post, we have discussed how to create an issue, labels, and milestones in GitLab project.
In this blog post, we will discuss how to add an SSH key in your GitLab profile to enable the cloning of the GitLab project repository using SSH.
Git is a distributed version control system, which means you can work locally but you can also share or “push” your changes to other servers. Before you can push your changes to a GitLab server you need a secure communication channel for sharing information.
The SSH protocol provides this security and allows you to authenticate to the GitLab remote server without supplying your username or password each time. GitLab supports RSA, DSA, ECDSA, and ED25519 keys. Their difference lies on the signing algorithm, and some of them have advantages over the others.
How To Add An SSH Key In Your GitLab Profile:
Step 1: Create an ssh key in your local system.
How To Add Ssh Key To Gitlab
Generate Ssh Key Windows
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 | ## Test your ssh ## Create a project in GitLab ## GitLab Console => Projects => New Project => <YOUR_PROJECT_NAME> PROJECT_ID=$(curl--silent--header'PRIVATE-TOKEN: <YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN>' -XPOST'https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects?name=cloudaffaire&visibility=private&initialize_with_readme=true'|jq'.id') ## Get the ssh clone url of your GitLab project repository ## GitLab Console => Projects => Your Projects => Clone => Clone with SSH SSH_CLONE_URL=$(curl--silent--header'PRIVATE-TOKEN: <YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN>' -XGET'https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/$PROJECT_ID'|jq-r'.ssh_url_to_repo')&&echo$SSH_CLONE_URL ## Clone your GitLab repository using ssh key |
Hope you enjoyed this article. In the next blog post, we will discuss Groups and Sub-Groups in GitLab.
Generate Ssh Key Gitlab
To get more details on GitLab you can follow the below link.
Gitlab Create Ssh Key
To Get more details on Git you can follow the below links.